Heat Stress Management
Heat - humidity Stress Management in Dairy Animals.-
The ideal temperature range for dairy cattle is between 25 and 65 degrees Fahrenheit. Once the temperature goes above 80 degrees Fahrenheit cattle reduce feed intake, which has a negative impact on production.
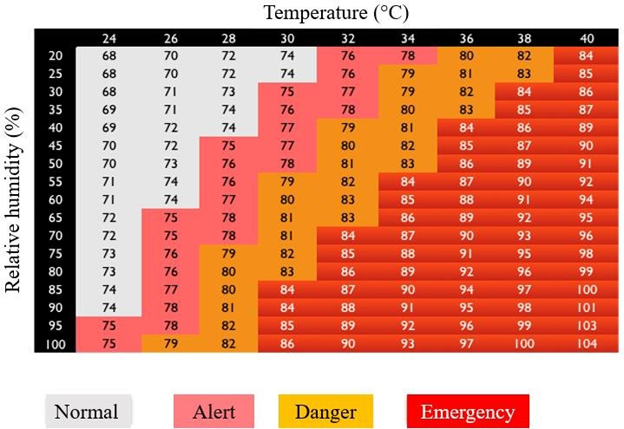
The changes in the environmental factors like ambient temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and solar radiation causes stresses in lactating cattle.
Heat stress is a condition in which the animal body has problems dissipating excess heat. Results of inadequate heat dissipation range from general discomfort to symptoms of heat rash, heat syncope, heat cramps, heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
Temperature Humidity Index (THI) is calculated based on the relationship between environmental temperature and relative humidity.
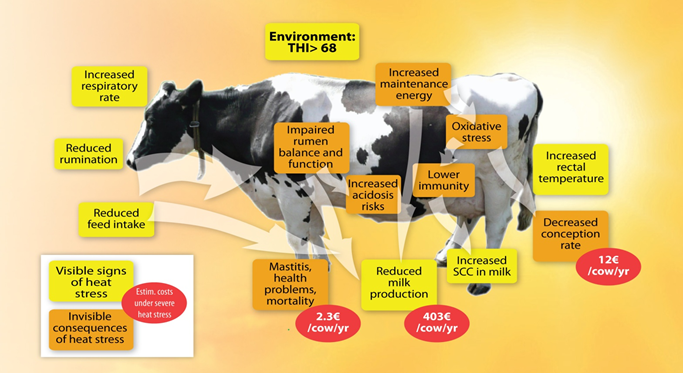
Effect of Heat Stress on Dairy Animals-
In hot weather, cattle may consume less feed. Reduced feed intake can cause ruminal acidosis and decrease the animal’s production of volatile fatty acids. This, in turn, reduces the cow’s energy levels and fat content in its milk.
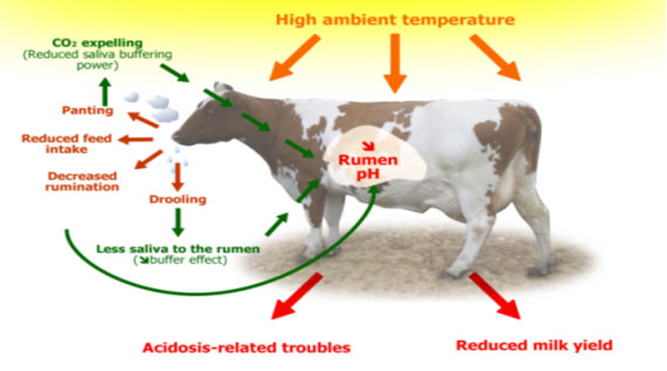
How Rumen health effected During Heat Stress-
We found that heat stress resulted in reduced pH and increased lactate level in the rumen fluid.
Higher production of lactate can decrease energy availability, reduce pH and then inhibit the growth of pH-sensitive ruminal bacteria (e.g., cellulolytic bacteria), and cause sub-acute ruminal acidosis.
High yielding cows more susceptible to heat stress than the low yielders.
Heat stress can increase body temperature which may affect the fat synthesis in mammary gland. Apart from reducing the milk production, heat stress can also reduce the quality of milk.
Heat stress markedly reduces DMI and milk yield and because the decreased DMI precedes the reduction in milk production, it is generally accepted that reduced nutrient intake is primarily responsible for the diminished milk synthesis (see reviews by Fuquay, 1981; Beede and Collier, 1986; West, 2003).
Tips to control Heat Stress:
Farmers can manage Heat stress pressure of animals to use below methods to in hot, humid and sunny weather.
- Shade
Shade can help reduce the solar heat load and remains one of the first recommendations to help lactating cows and dry cows manage their heat load in hot weather. - Cooling with water
Sprinklers and misters help cows get rid of body heat.
• Sprinklers wet the cow’s skin, and her body heat is used to evaporate the liquid water on the skin.
• Misting systems cool the air by evaporating water droplets using heat in the air. - Drinking water
Hydration is incredibly important for a cow to regulate body temperature, both during times of heat stress and cold stress. Adequate drinking water should be supplied at all times.
Water troughs should be at least three inches deep to allow cows to submerge their muzzle when drinking.
Cows consume up to 50% of their daily water intake following milking.
Make sure water flow to the trough and water capacity is adequate to account for large quantities needed at all at once.
Holding area cooling
Milking center holding areas need special attention paid to ventilation and cooling in warm weather to avoid heat stress.
Cows can be crowded in the holding area for up to an hour. A crowded pen reduces the airflow around a cow and can make it more difficult for her to avoid heat stress.
Nutritional management
Provide high quality feeds like total mixed rations. Increase the frequency of feedings and Feed during cooler times of the day.
In addition to the above practices, we would like to suggest dairy farmers to feed AnniZymeX or Rumyst @ rate of 10 gm/day/animals, so that the negative effects of heat stress can be easily overcomes.
AnniZyme X and Rumyst Help Dairy animals to minimize effect of Heat stress to improves the-
Rumen and Rumen microbial health.
Feed intake.
Metabolism.
Body condition score.
Antioxidant status.
Milk production and quality.
Overall comfort of animals.
For more product information visit the product page.
